Technology Type
- Type
- Gas Phase Polymerization of Propylene
- Process
- Polypropylene processes
- Abbreviation
-
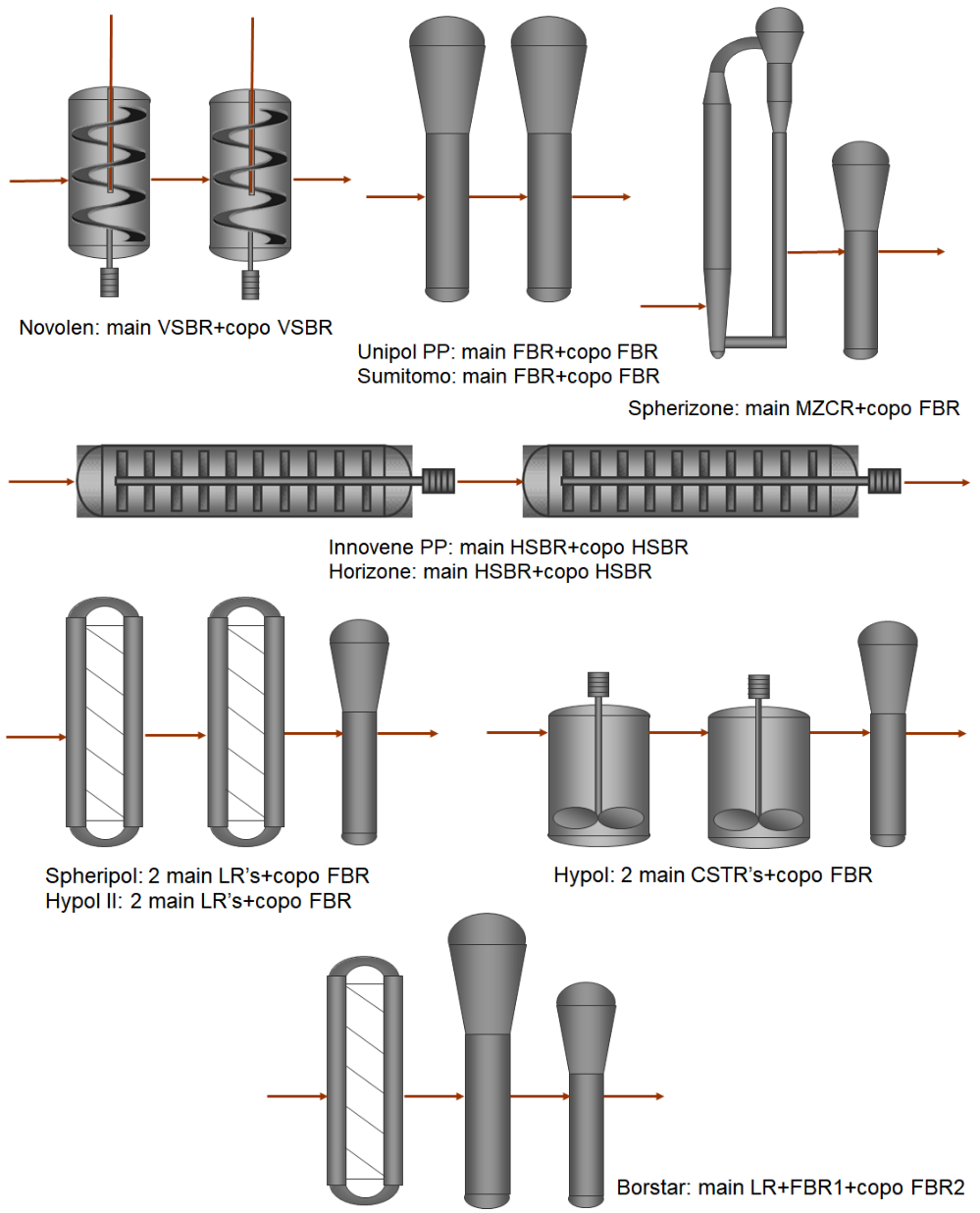
In Gas Phase processes, Gaseous Propylene comes into contact with the Solid Catalyst which is intimately dispersed in Dry Polymer Powder. The typical feature of this process is the Fluidized Bed Reactor which widens at its top to reduce the Gas Velocity and Entrainment of Particles. Continuously fed flows of Catalyst, Monomer and Hydrogen are mixed thoroughly in the Fluidized Bed. A large Cooler in the Loop for Gas Recirculation draws off the Reaction Heat from the considerable Gas Volume Flows. In this system, the Fluidized Bed Reactor acts like a Back-Mixing Autoclave Reactor; there is no excessive Separation of Coarse Particles. For Copolymerisation, a second Fluidized Bed Reactor is added. The Reaction Conditions are below 88 °C and 4 MPa. The Polymer and associated Gases are discharged from the Reactor directly above the Distributor Plate with Time-Controlled Valves passing through a Cyclone into a Tank filled with Nitrogen to remove residual Monomers from the Polymer.
Examples of pure Gas-Phase Polymerization Technologies in Stirred Bed Reactors (SBR) or Fluidized Bed Reactors (FBR) are the Novolen, Unipol PP and Innovene PP Processes.
Source: European Commission, Aug 2007, Reference Document on Best Available Techniques in the Production of Polymers, DOCPLAYER - Link
System Info
- Updated by
-
 Kokel, Nicolas
Kokel, Nicolas - Updated
- 5/1/2024 6:24 PM
- Added
- 11/13/2021 4:08 PM

No Services yet available.
Enquire in Solutions how we can help you.
Technology Type Communicator
| Title | Date |
|---|
Image
Technologies
| Technology | Owner | |
|---|---|---|

|
Grace | |

|
Ineos Techn Holdings | |

|
Lummus | |

|
Sumitomo Chemical |