Process Chemistry
The OMEGA Process ("Only MEG Advantage") is a Process by Shell Global Solutions that is used to produce Ethylene Glycol from Ethylene. This process comprises two steps, the controlled Oxidation of Ethylene to Ethylene Oxide (EO), and the net Hydrolysis of Ethylene Oxide to Monoethylene Glycol (MEG)[1]. The present technology review only deals with this second process stage.
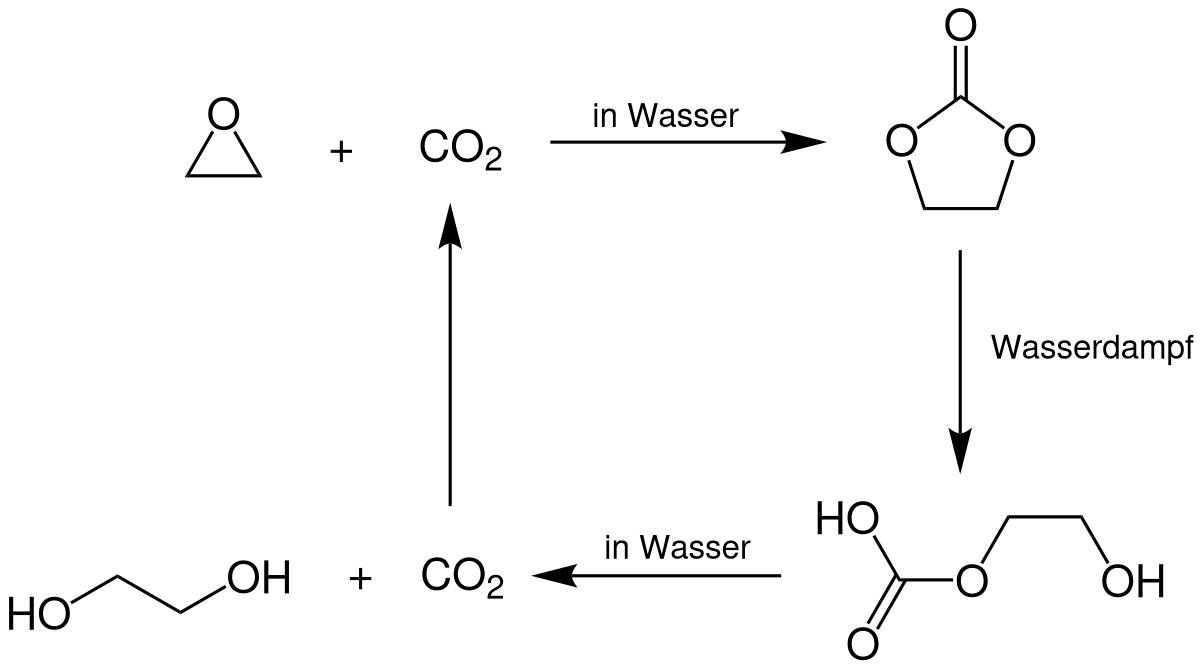
In the OMEGA process, the ethylene oxide reacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) to yield ethylene carbonate (C3H4O3) according to equation (a). Ethylene carbonate is subsequently hydrolyzed to monoethylene glycol and carbon dioxide according to equation (b). The carbon dioxide is released in this step again and can be fed back into the process circuit. This process is 99.5% selective for monoethylene glycol[1].
| |
(a) |
C2H4O + CO2 → C3H4O3 |
| |
(b) |
C3H4O3 + H2O → HOC2H4OH + CO2 |
| |
|
|
Shell’s OMEGA process for producing mono-ethylene glycol (MEG) from ethylene is a 2-stage, fully catalytic process, which has enabled many operators to achieve a conversion efficiency of over 99% compared to around 90% for conventional processes which utilise a thermal route to convert ethylene oxide (EO) into MEG. For every tonne of ethylene, operators with OMEGA have produced up to 1.95 tonnes of MEG compared with conventional processes which produce between 1.53 tonnes to 1.70 tonnes[2].
Process Flow Diagram
The two-stage OMEGA process is depicted in Fig. 1, whereby the MEG process stage starts from item nr. ⑥ (carbonation reactors). This part of the process is itself made of two sections: ethylene glycol synthesis and ethylene glycol purification[3].
(1) Ethylene oxide synthesis:
Ethylene oxide is reacted with CO2, forming ethylene carbonate, which is then hydrolyzed to form MEG and CO2. Both reactions are carried out in the liquid phase using homogeneous catalysts. CO2 streams from the reaction steps are recycled to the ethylene carbonate reactor[3].
(2) Ethylene oxide purification:
MEG produced is purified in two distillation columns where water is removed, leading to the final MEG product. The homogeneous catalyst is separated and recycled to the ethylene carbonate reactors[3].
Figure 1 - Ethylene Glycol via Carbonation of EO Simplified PFD[3].

Legend: ⑥ Ethylene carbonate reactors; ⑦ Hydrolysis reactors; ⑧ Water removal column; ⑨ MEG purification column; ⑩ CW: Colling water; ⑪ ST: Steam.
Process Licensing and Plant References
This part of the OMEGA process was originally developed by Mitsubishi Chemicals, and it has been exclusively licensed to Shell[1]. The first Chemical Plant using the OMEGA Process was started in South Korea. Subsequent OMEGA plants have been started in Saudi Arabia and Singapore[2].
References
- Wikipedia, OMEGA process, (accessed 29th Apr 2024).
- Shell, OMEGA process (accessed 29th Apr 2024).
- Intratec Solutions, 14th Sep 2023, Ethylene Glycol from Ethylene (Carbonation without EO By-Product) | Economic Analysis, Medium.