Process Description
In the standard thermal glycol reaction process, ethylene oxide (EO) and water are reacted at an elevated temperature and pressure without catalyst to to produce an Ethylene Glycols mixture. The reaction takes place at a temperature of 200°C, a pressure of 12.5 bar with a residence time of one hour.[1,2].
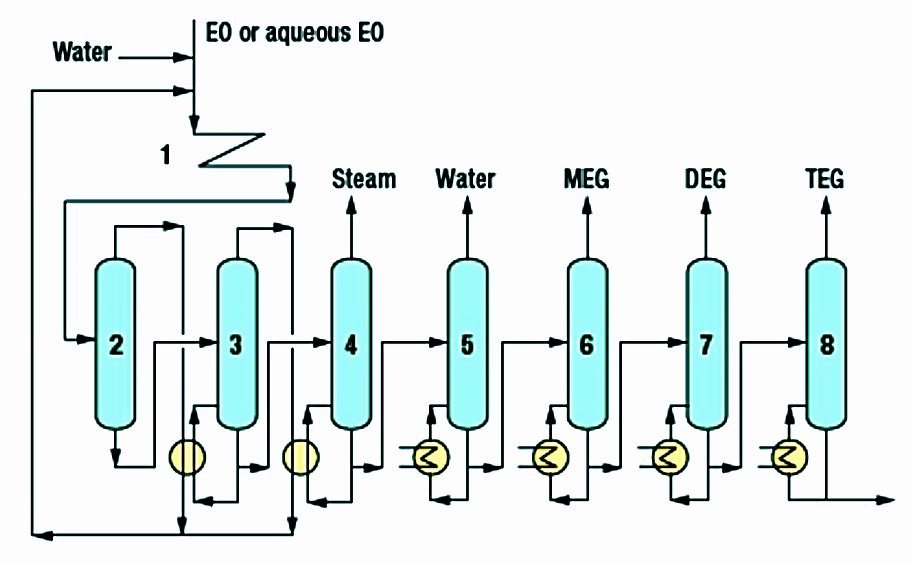
In the tubular reactor ①, essentially all EO is thermally converted into monoethylene glycol (MEG) with diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) as co-products in minor amounts. The crude glycol mixture contains 75-92 wt% MEG. The selectivity to MEG can be influenced by adjusting the glycol reactor feed composition but heavier glycol formation is inevitable since EO reacts more readily with MEG than water, therefore excess water is used to minimize the reactions.[1-3].
The water–glycol mixture from the reactor is then fed to multiple evaporators (②,③,④) where the excess water is recovered and largely recycled. The last evaporator produces low-pressure steam that is used as a heating medium at various locations in the plant[1,3].
After drying (⑤), the crude glycol mixture undergoes successive purification and distillation in a series of vacuum columns (⑥,⑦,⑧) where heavier glycols are recovered in decreasing yields. The glycols are cooled and routed to storage[2,3].
Energy and Material Flows
Energy and Material Flows of the Ethylene Oxide and Ethylene Glycols processes in Mordijk, The Netherlands, are presented in Table 1[3]:
Table 1 - Energy and Material Flows of the SHELL EO/EG Process in Mordijk, The Netherland.
| Ethylene Oxide |
Mass (kt/year) |
Energy (pJ/y) |
| INPUTS |
|
|
| Ethylene |
218 |
|
| Oxygen |
276 |
|
| OUTPUTS |
|
|
| Ethylene Oxide |
305 |
|
| CO2 (partly exported) |
75 |
|
| ENERGY |
|
|
| Steam |
net export |
-1.5 |
| Electricity |
|
0.31 |
| ETHYLENE GLYCOLS |
|
|
| INPUTS |
|
|
| Ethylene Oxide |
122 |
|
| OUTPUTS |
|
|
| Ethylene Glycols |
155 |
|
| ENERGY |
|
|
| Steam |
|
0.7 |
| Electricity |
|
0.04 |
| Fuel Gas |
3 |
0.1 |
| CO2 |
9 |
|
| Total CO2 |
85 |
|
Process Licensing
Shell has issued licenses for 89 EO/EG plants worldwide, 53 of which are still operating[4].
References
- Shell Catalysts & Technologies, 22nd Mar 2021, ENHANCEMENTS IN ETHYLENE OXIDE/ETHYLENE GLYCOL MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER.
- Louise Wong, Ton van Dril, 9th Nov 2020, Decarbonisation Options for Large Volume Chemicals OProduction, Shell Mordijk, PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency.
- Jack, 5th Jun 2018, Ethylene Glycols (EG) Process by Shell Global Solutions International B.V., Oil & Gas Process.
- Shell, MASTER (EO/EG) Process (accessed 29th Apr 2024).