Process Summary
The ethylbenzenzene dehydrogenation technology developed by Ruihua Technology is described in a series of patents comprising a process method for producing styrene[1], equipment for ethylbenzene and styrene separation[2], and a method for refining styrene[3].
Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation Process
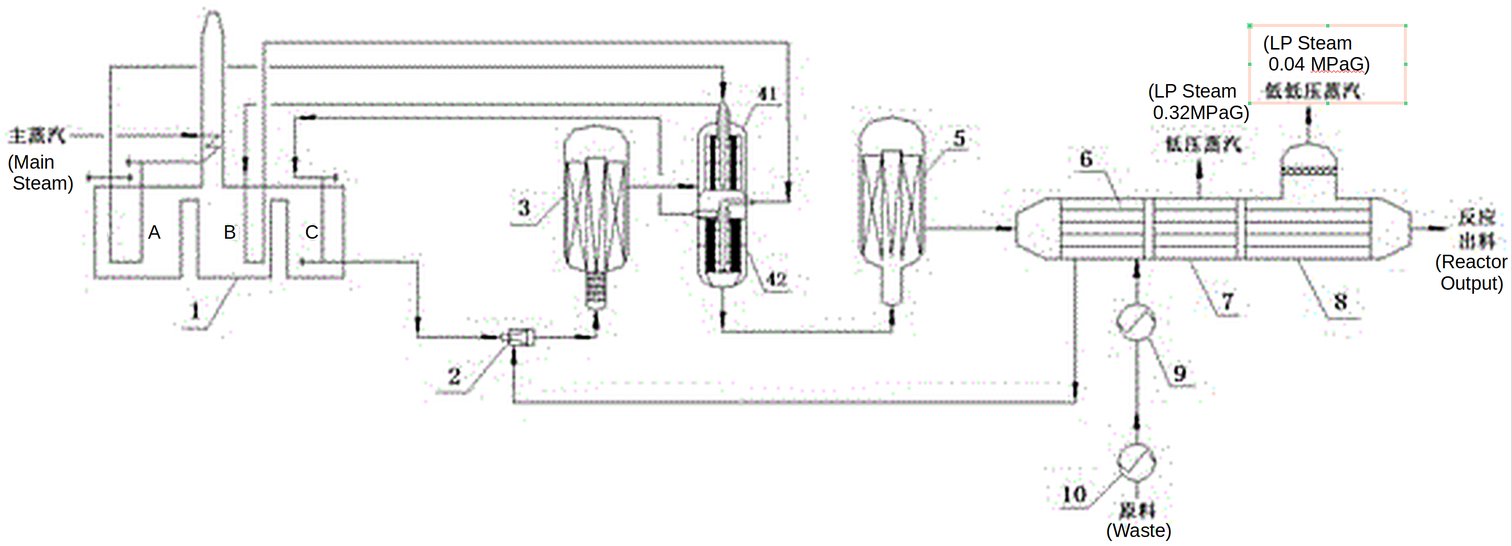
The ethylbenzene dehydrogenation technology is presented in Fig. 1 according to CN111848323A[1].
Figure 1 - Ruihua Technology ethylbenzene dehydrogenation process flow diagram.
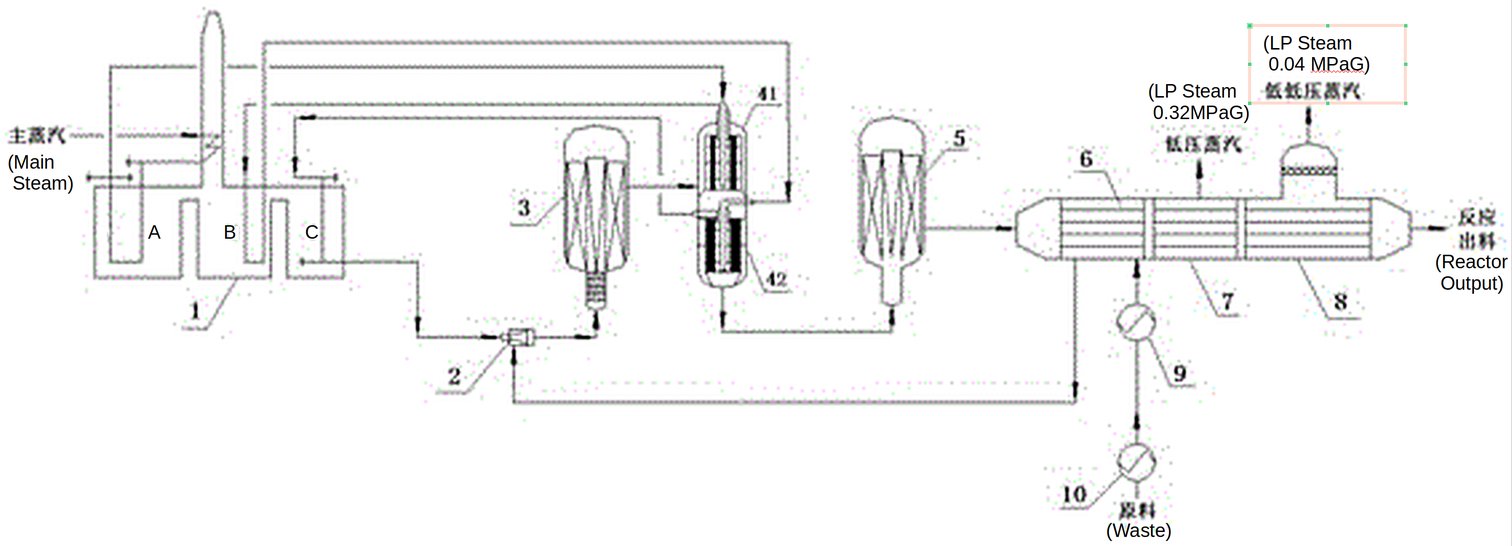
Legend: 1. Steam Heating Furnace (three-chamber heating type); 2. Premixer; 3. & 5. Hydrogenation reactors; 4. Heat exchanger (41. Upper tube pass, 42. Lower tube pass); 6. Ethylbenzene superheater; 7. & 8. LP steam generator; 9. Ethylbenzene preheater 10. Ethylbenzene evaporator.
The process method for producing styrene by low water ratio ethylbenzene dehydrogenation comprises the following steps:
- The main steam is sequentially heated in three stages through a chamber A, a chamber B and a chamber C of the steam heating furnace 1, wherein the heat of the steam in the chamber A and the chamber B is transferred through a heat exchanger 4 to provide heat for the second-stage dehydrogenation reaction. The temperatures of the main steam flowing out of the chamber A, the chamber B and the chamber C are respectively about 805 ℃, 835 ℃ and 870 ℃.
- After ethylbenzene is evaporated in the shell pass of evaporator 10 an ethylbenzene-steam mixture with the temperature of about 95 ℃ is obtained. The ratio of the raw material low-pressure steam to the ethylbenzene is 0.35.
- The mixture is further heated to 142 ℃ through a preheater 9. Low pressure steam is supplied to the preheater 9 for heating the feedstock.
- The ethylbenzene-steam mixture then enters an ethylbenzene superheater 6 in the shell pass, where it is heated to 532 ℃ by reaction gas with the temperature of about 566 ℃ which just flows out from a second dehydrogenation reactor 5 in the tube pass.
- The ethylbenzene-steam mixture enters a premixer 2 and is mixed with main steam of 870 ℃ from a chamber C of a steam heating furnace 1. The temperature reaches 615 ℃ after mixing, and the water ratio of a first mixed material formed after mixing is 0.85.
- The first mixed material immediately enters a first dehydrogenation reactor 3, and ethylbenzene is subjected to dehydrogenation reaction in a catalyst bed layer under negative pressure adiabatic condition; because the ethylbenzene dehydrogenation reaction is an endothermic reaction, the temperature of the first dehydrogenation material flowing out of the first dehydrogenation reactor 3 is reduced to about 522 ℃;
- The first dehydrogenation material subjected to the first-stage dehydrogenation reaction enters an upper 41-tube pass of heat exchanger 4, exchanges heat with 805°C superheated steam from a chamber A of the steam heating furnace 1 on a shell pass, and the temperature of the reaction material on the tube pass is increased to 573 ℃.
- Then the mixture enters a lower section 42 tube pass of the heat exchanger 4 to exchange heat with 835 ℃ superheated steam from a B chamber of the steam heating furnace 1 in a shell pass, the temperature of a first dehydrogenation material in the tube pass is raised to 623 ℃.
- The mixture enters a catalyst bed layer of a second dehydrogenation reactor 5 to realize a second-stage negative-pressure adiabatic dehydrogenation reaction, and a second dehydrogenation material with the temperature of 565 ℃ is formed from a second dehydrogenation reactor.
- The second dehydrogenation material firstly enters the tube side of an ethylbenzene superheater 6 to exchange heat with the raw material, which reduces its temperature to 310 ℃.
- This second dehydrogenation material then enters the tube side of a low-pressure steam generator 7 to heat boiler feed water of the shell side, which generates low-pressure steam with the temperature of 152 ℃ at 0.32MPaG in the shell side, and the temperature of a reaction product is reduced to 156 ℃.
- The 156°C dehydrogenation material then enters the tube pass of a low-pressure steam generator 8 to generate low-pressure steam at 0.04MPaG on the shell pass, and the temperature of the reaction product is reduced to about 120 ℃ and then it is discharged out of the reaction system.
Ethylbenzene and Styrene Separation
The ethylbenzene and styrene separation technology is presented in Fig. 2 according to CN212655718U[2].
Figure 2 - Ruihua Technology ethylbenzene and styrene separation process flow diagram.
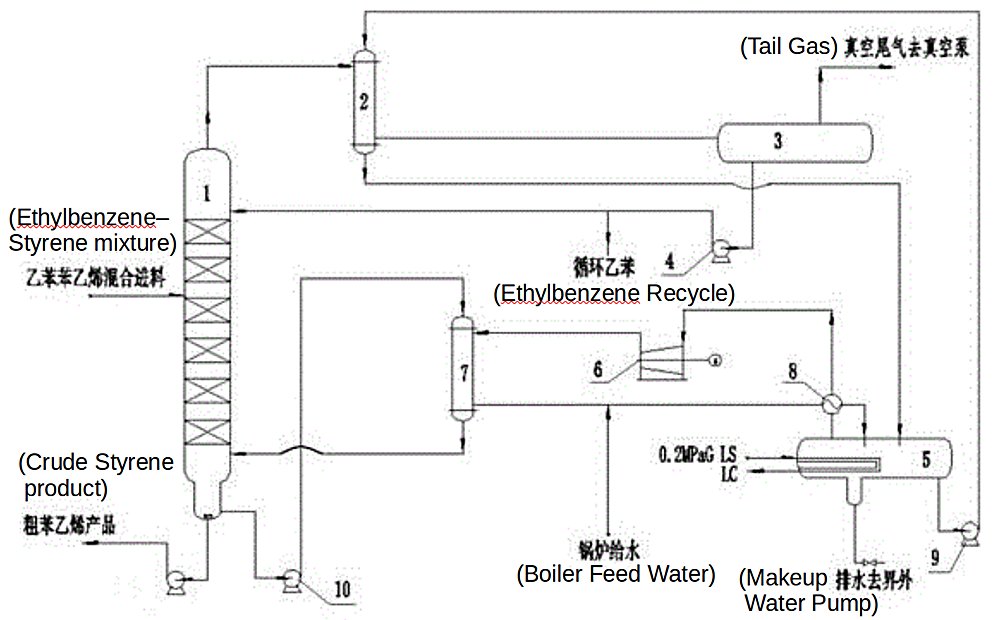
Legend: 1. Separation tower; 2. Tower top condenser; 3. Reflux tank; 4. Reflux pump; 5. Condensate evaporation tank; 6. Vapor compressor; 7. Tower kettle reboiler; 8. Superheater; 9. Condensate pump; 10. Circulation pump.
The process method for separating styrene from ethylbenzene comprises the following steps:
- The ethylbenzene and styrene mixed material is fed to the upper part of the separation tower 1.
- The ethylbenzene distilled out of the top of the separation tower enters a shell pass of condenser 2, that exchanges heat with condensed water added at the top of a tube pass of the condenser.
- The condensed ethylbenzene enters a reflux tank 3.
- Part of condensed liquid discharged from the reflux tank is used as reflux liquid returned to the top of the separation tower 1 via the reflux pump 4.
- The other part of the ethylbenzene is returned to the reaction unit as circulating ethylbenzene for recycling.
- Part of condensed water in the tube pass of the condenser 2 is vaporized to form a gas-liquid mixture, that is fed to a condensate evaporation tank 5 to realize gas-liquid separation.
- Water vapor enters a vapor compressor 6 after being overheated by a heat exchanger and is further pressurized to 0.18MPaG, then enters the shell pass of a kettle reboiler 7 and heats kettle liquid sent by the circulating pump 10 of the separation tower 1.
- Meanwhile, the water vapor condensed in the kettle reboiler is returned to the condensate evaporation tank 5.
- The condensed water in the condensate evaporation tank 5 is pressurized by the condensate pump 9 and recycled as vaporized materials to the condenser 2.
- The condensate evaporating tank 5 is provided with a steam generator for evaporating steam to supplement heat required by the reboiler 7.
- The material entering the reboiler 7 tube side through the circulating pump 10 is heated by the low-pressure steam of the shell side to form a gas-liquid two-phase mixture.
- The gas-liquid separation is realized by returning the gas-liquid two-phase mixture to the separation tower kettle 7.
- The qualified crude styrene separated from the discharge port of the separation tower kettle 7 is discharged through the discharge pump of the tower kettle.
Refining of Styrene
Crude styrene is refined by refining method having a combination of a falling-film reboiler and heat pump technology as disclosed in WO2023050988A1[2].
Industry References
The following references are reported by Rukai Chemical[4], a wholly owned subsidiary of Ruihua Technology[5]:
- Xinyang Technology Group Co., Ltd. 600,000 tons/year ethylbenzene 300,000 tons/year styrene plant
- 200,000 tons/year styrene plant of Shandong Heze Yuhuang Chemical Co., Ltd.
- 100,000 tons/styrene plant of Changzhou Donghao Chemical Co., Ltd.
- 200,000 tons/year styrene plant of Ningbo Keyuan Plastic Co., Ltd.
- 60,000 tons/year styrene plant of Lijin Petrochemical Plant Co., Ltd.
- POSM co-production plant of Dongming CITIC Guoan Ruihua New Materials Co., Ltd.
- 60,000 tons/year styrene plant of Shandong Shengyuan Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
- Abel Chemical (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. 300,000 tons/year styrene plant
- Anhui Haoyuan Chemical Group Co., Ltd. 260,000 tons/year styrene plant
- 350,000 tons/year styrene plant of Liaoning Baolai Chemical Co., Ltd.
- 80,000 tons/year styrene plant of Hebei Shengteng Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Anhui Jiaxi New Materials Co., Ltd. 350,000 tons/year styrene plant
- Tangshan Xuyang Aromatics Products Co., Ltd. 300,000 tons/year styrene plant
- 400,000 tons/year styrene plant of Ningbo Huatai Shengfu Polymer Materials Co., Ltd.
- 120,000 tons/year styrene plant of Sinochem Hongrun Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Zhejiang Petrochemical Co., Ltd. 270,000 tons/year propylene oxide co-production 600,000 tons/year styrene plant
References
- 和成刚 et al., Priority: 26th May 2020, CN111848323A, Process method for producing styrene through ethylbenzene dehydrogenation with low water ratio, assigned to Changzhou Ruihua Chemical Eng & Tech Co ltd.
- 和成刚 et a., Priority: 14th May 2020, CN212655718U, Low-energy-consumption complete equipment for ethylbenzene and styrene separation, assigned to Changzhou Ruihua Chemical Eng & Tech Co ltd.
- 张晶 et al., Priority: 27th Jul 2022, WO2023050988A1, Method for refining styrene by using combined falling film reboilers and heat pump technology to provide heat source of separation column, assigned to Changzhou Ruihua Chemical Engineering Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ruihua Chemical, Company Profile. (accessed 6th Nov 2024)
- Ruiha Chemical, Dehydrogenation reactor. (accessed 6th Nov 2024)