Urea Synthesis[1]
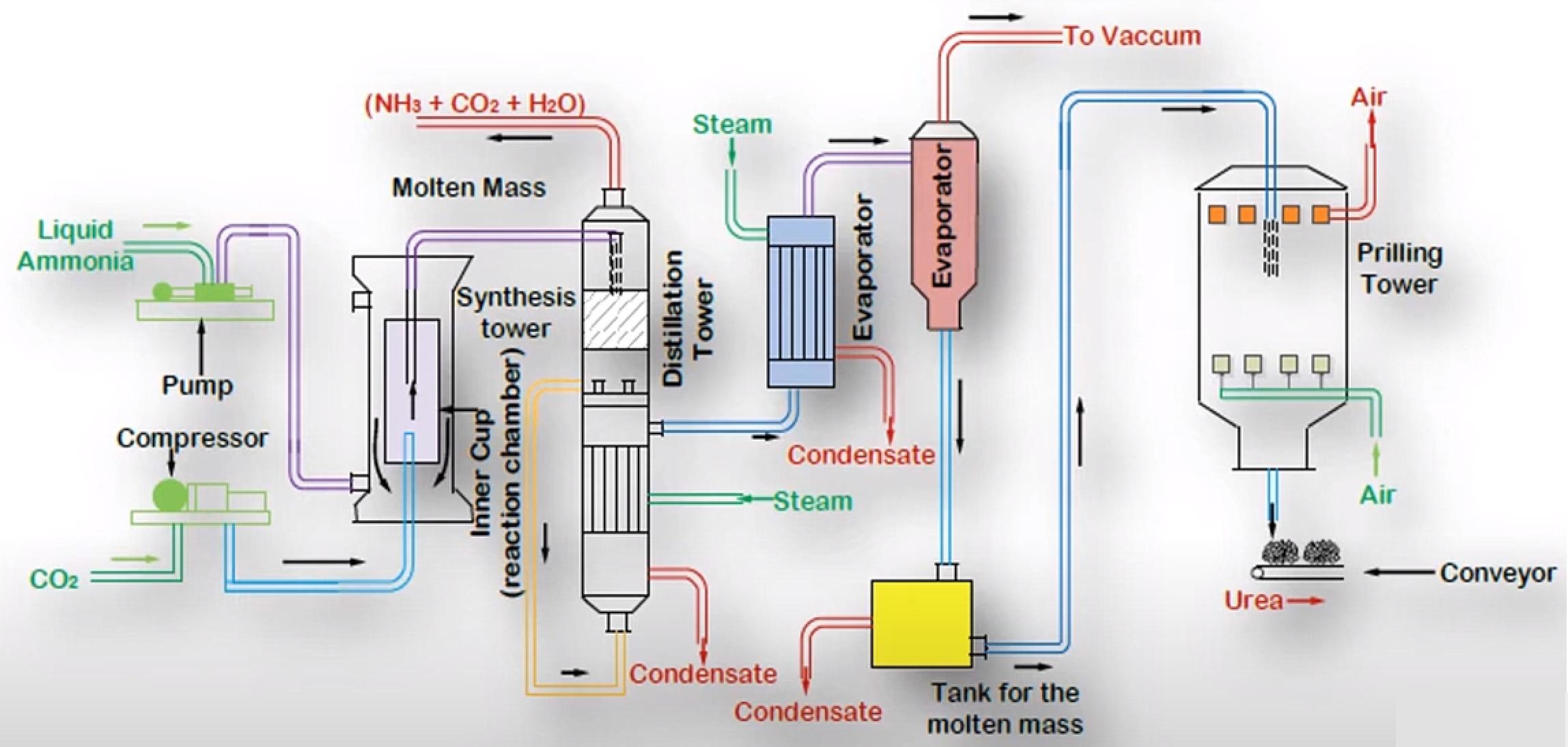
Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide are the Raw Materials for the Urea Manufacturing Process; usually, Urea is manufactured in an Ammonia Plant because it yields Ammonia as a Product and Carbon Dioxide as a Byproduct and this Carbon Dioxide can be recycled directly into the Process.
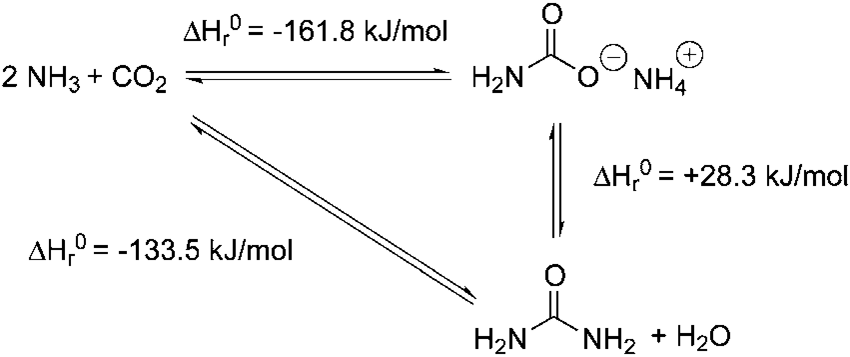
The Chemical Reactions involved in the Process are:
- The reaction of Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide to form Ammonium Carbamate*:
2 NH3 + CO2 → H2N-CO2- NH4+ (Ammonium Carbamate)
- Decomposition of Ammonium Carbonate to form Urea and Water*:
H2N-CO2- NH4+ → H2O + H2N-C(O)-NH2 (Urea)
*Note: both Reaction equations above are reversible.
Figure 1 - Reactions during Urea Synthesis[2]
Process Details[1]
Liquified Ammonia is pumped and compressed Carbon Dioxide is fed into a Reaction Chamber. The Reactor is the Heart of the Process where the Reactions happen. The reactor is maintained at 14Mpa pressure and 170-190°C for the first Reaction to occur. The Condensation of Ammonia with Carbon Dioxide is highly exothermic. Most of the heat released is utilized in the form of Process Steam wherever it is needed in the Process.
The Product from the first Reaction flows into a Decomposer where the second Reaction occurs. As it is an endothermic Reaction it requires energy input to be started. Biuret is also formed as a result of Decomposition of Ammonium Carbamate if the temperature rise is excessive.
Figure 2 - Urea Manufacturing Process[3]
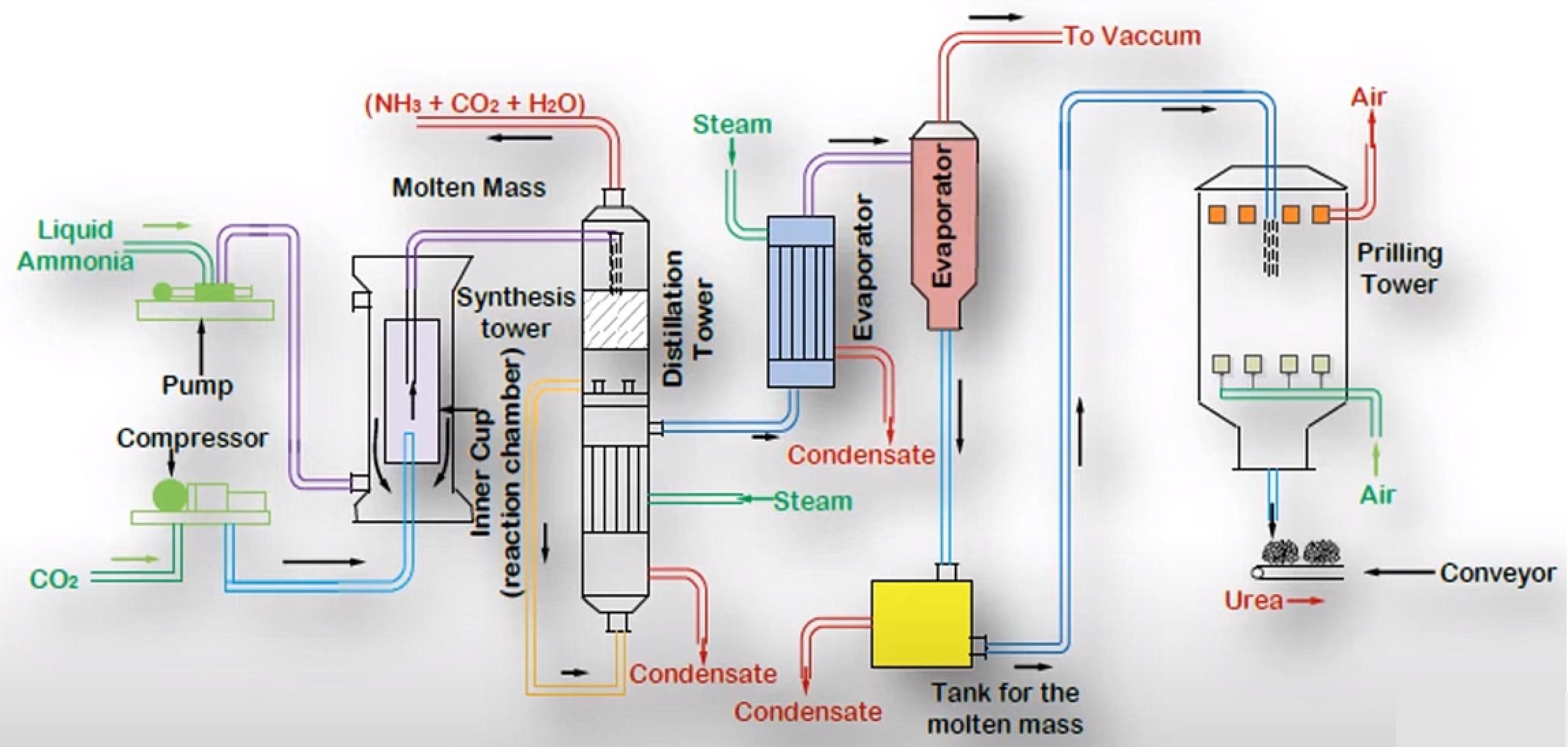
The Conversion of the Reactants to Urea can be increased by increasing the amount of Carbon Dioxide. With Carbon Dioxide present in excess the Conversion can be as high as 85% per pass but optimizing for the proper temperature, pressure and design is a challenge in itself, hence usually per pass Conversion is kept at around 50%. The unreacted Materials are recycled, resulting in overall Conversion of over 99%.
The major Impurity in Urea is Water together with unreacted Ammonia, Carbon Dioxide and Ammonium Carbamate. These are removed in the Distillation Tower and the Evaporator. The essential condition is to keep the temperature high and pressure low during Stages of Separation. Under these conditions, the Ammonium Carbamate decomposes back to Ammonia and Carbon Dioxide, with some of the Carbon Dioxide and Ammonia being flashed off. The primary Process taking place in the evaporator is that of Concentration. During Concentration, optimum temperature should be maintained so that the Urea remains in molten state and crystals are not formed inside the Evaporator.
The molten Urea is passed through Nozzles inside the Prilling Tower. Compressed Air is passed in the Tower so that its flow is counter-current with respect to that of Molten Urea. The Urea gets solidified in the Prilling Tower, and Air helps in shaping it in the form of Prills or Granules. The Urea is then stored and ready to be sold.
Commercial Technologies
Some commercial Urea Manufacturing Technologies are:
- Saipem - Snamprogetti Urea Process
- Stami Carbon - Stami Urea
- Thyssenkrupp Uhde - Urea 2000plus
- Toyo Engineering - ACES21®
References
1. EBL Engineering Ltd., 25 Oct 2020, The Urea Manufacturing Process, eblprocesseng.com
2. An overview of CO2 capture technologies - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from:https://www.researchgate.net/figure/ndustrial-synthesis-of-urea-from-CO-2-and-thermodynamics-of-the-process_fig11_265122194 [accessed 7 Feb, 2023]
3. Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology, 2022, Urea Manufacturing Process, Youtube