Main-Product
- Product
- Polyethylene
- Segment
- Chemicals
- Main-Family
- Polymers
- Sub-Family
- Polyolefins
- Link
-

- #PS58
Description
Insights from our Experts
|
2025/12/15 10:42 AM
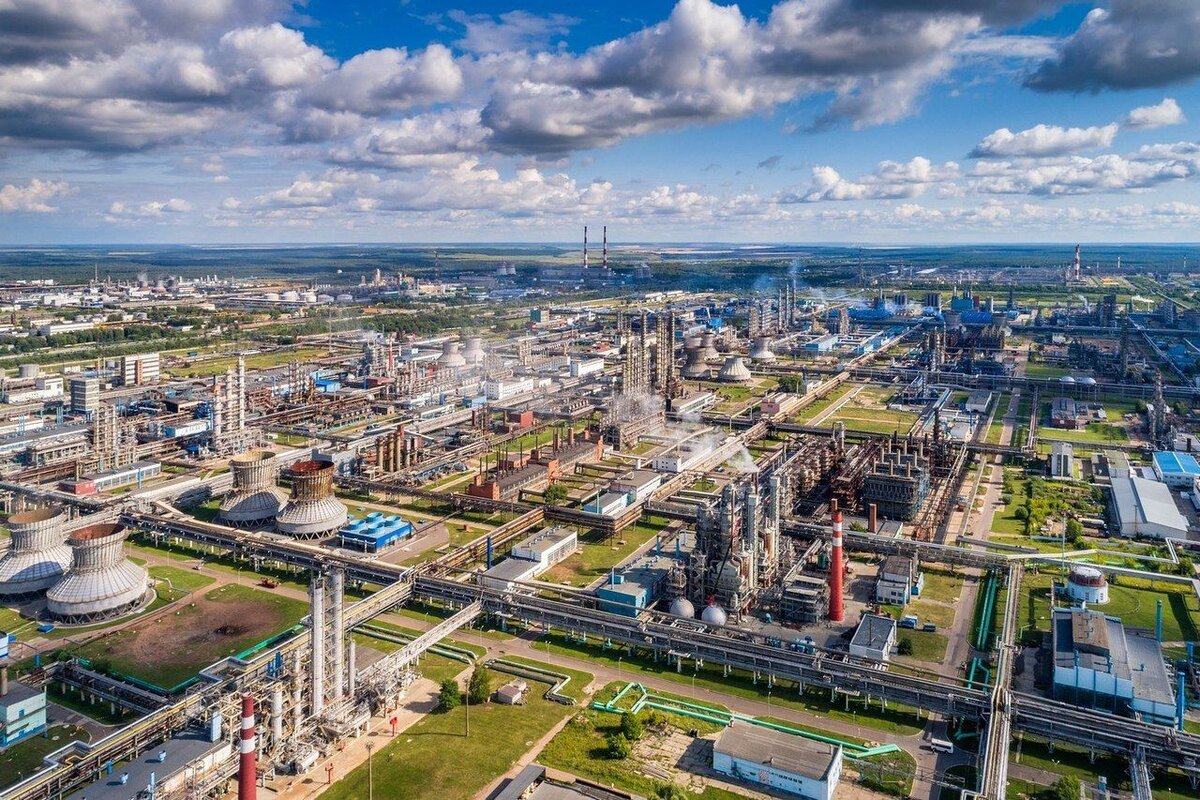
Article image: Nizhnekamskneftekhim facility from public sources Nizhnekamskneftekhim deployment marks Russian petrochemical industry's push for comonomer self-sufficiency... |
Product Communicator
(*=Default)| Product | Title | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
5/14/2025 | ||

|
2/9/2025 | ||

|
10/28/2024 | ||

|
10/28/2024 | ||

|
5/27/2023 | ||

|
9/26/2021 | ||

|
9/26/2021 | ||

|
9/26/2021 | ||

|
9/26/2021 |
| Products (Quick Access) | Abbr. | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | PE | |
| C4-LLDPE | C4-LLDPE | |
| C6-LLDPE | C6-LLDPE | |
| C8-LLDPE | C8-LLDPE | |
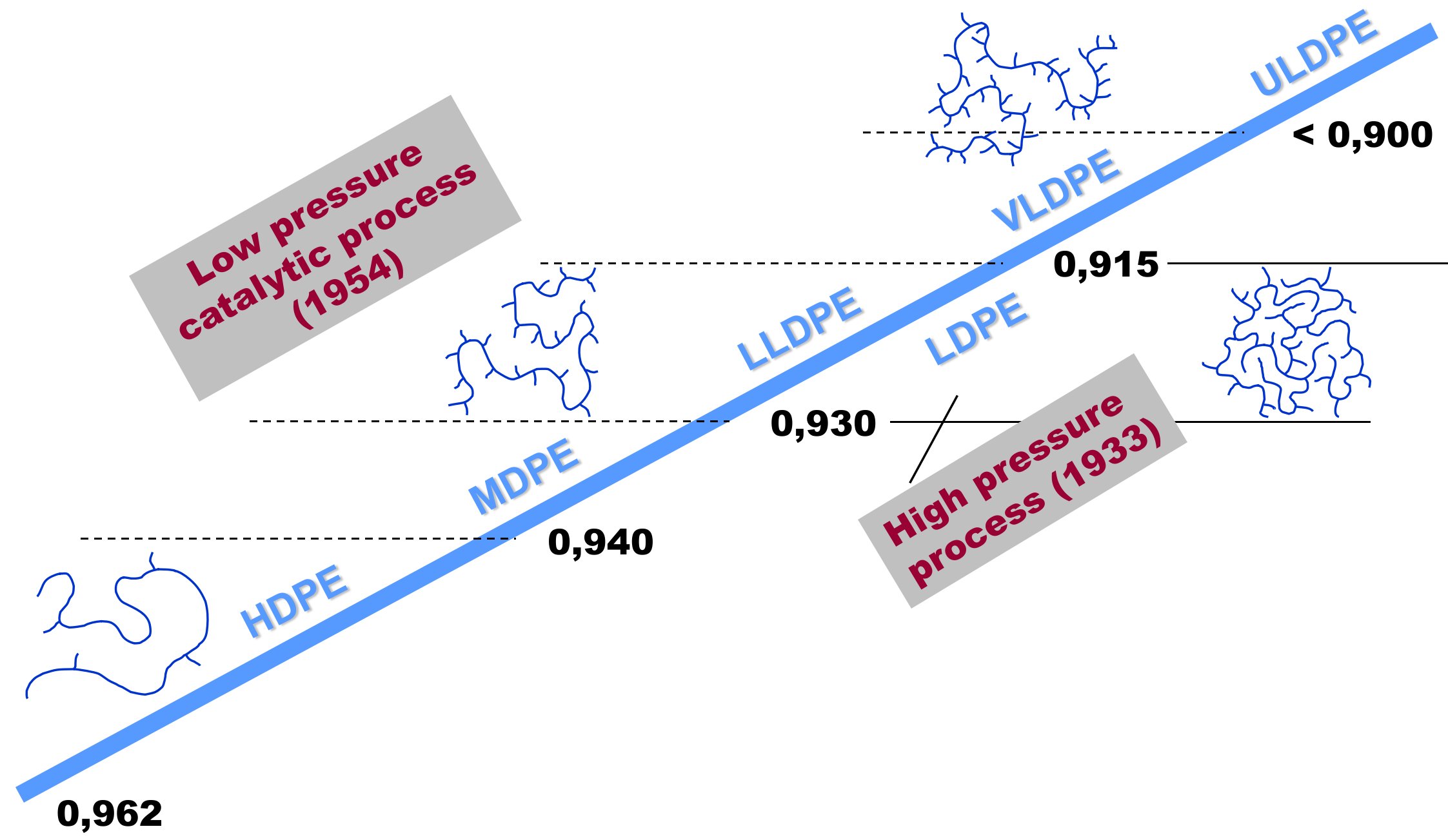
| Full Density Range Polyethylene | FDPE | |
| High-Density Polyethylene | HDPE | |
| Linear Low Density Polyethylene | LLDPE | |
| Low Density Polyethylene | LDPE | |
| Medium-Density Polyethylene | MDPE |
Settings
- Status
- A
- Unit of Measure
- Metric Ton
- Physical State
-
Solid
Building Block / Value Chain Info
- Value Chain-I
- Ethylene
Content provided by
| Transaction | Name | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Modified by |
|
2/9/2025 5:22 PM |
| Added | 2/15/2021 12:02 PM |