Direct Hydrolysis of Ethylene Oxide Reaction
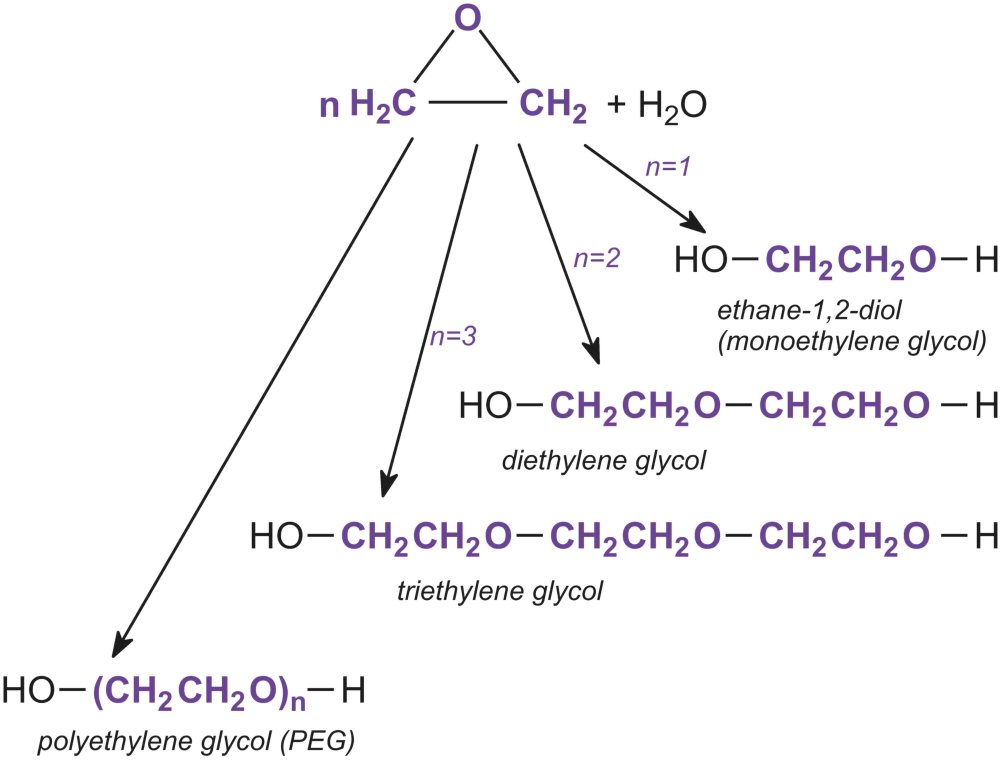
Ethylene Oxide is reacted with Water under neutral or acidic conditions, to form stepwise a range of products (Fig. 1)[1]:
- When n = 1, the product is ethane-1,2-diol often known as monoethylene glycol HOCH2CH2OH, used in engine coolants, in heat transfer fluids, and for production of polyesters such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate).
- When n = 2, the product is HOCH2CH2OCH2CH2OH, usually known as diethylene glycol. It is used principally to make polyurethanes and polyesters.
- When n = 3, the product is HOCH2CH2OCH2CH2OCH2CH2OH, also known as triethylene glycol and which is is used as a plasticiser.
- When n = 4 or more, the product is a poly(epoxyethane), known usually as polyethylene glycol (PEG). These are classified by relative molecular mass, PEG200, PEG400, PEG600, etc. and are used as nonionic surfactants, synthetic lubricants and solvents for paints. They are also used in cosmetics and are used as plasticisers in adhesives and printing inks.
Figure 1 - Production of ethylene glycols.
This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the Oligomers, and Tetraethylene Glycol[2].
Process Description
The process comprises two major sections (Fig. 2): (1) Ethylene glycol synthesis; and (2) Ethylene glycol purification[3].
- Ethylene Glycol Synthesis
The ethylene oxide is combined with water, heated and fed to a tubular reactor, where the ethylene oxide is thermally hydrolyzed to Ethylene Glycol without a catalyst. As ethylene oxide reacts with ethylene glycols more quickly than with water, diethylene glycol (DEG), triethylene glycol (TEG) and heavy glycols are also formed. The yields of such glycols, however, are minimized by conducting the reaction in excess of water, what ultimately improves selectivity towards MEG[3].
- Purification Section
The excess of water used in the EG reaction is removed from the reactor outlet by means of a multi-stage evaporator. Then, the MEG is purified in successive distillation steps, while residual water is recycled to the reactor as process condensate and DEG and TEG are recovered as by-products[3]. However, the separation of these oligomers and water is energy-intensive[2].
Figure 2 - Simplified PFD of Ethylene Glycols from Ethylene Oxide Direct Hydrolysis
.png)
Legend: 1. EG reactor; 2. EG evaporator; 3. Dehydration Column; 4. MEG column; 5. DEG column; 6. TEG column; 7. CW: Cooling water; 8. ST: Steam.
Mass Balance
A typical mass balance of an integrated EO/EG process is provided in the literature as shown in Table 1[4]:
Table 1 - Typical Inputs and Outputs at End Run of the Ethylene Oxide process / EO Direct Hydrolysis Process.
Component
Input |
Flow Rate
(kg/t of EO) |
Component
Output |
Flow Rate
(kg/t of EO) |
| Ethylene |
824.43 |
Carbon Dioxide |
564.02 |
| Oxygen |
980.43 |
MEG |
1233.62 |
| Water |
151.28 |
DEG |
126.19 |
| Nitrogen** |
0.18 |
TEG |
22.32 |
| Argon** |
6.42 |
Ethylene* |
26.23 |
| Methane |
8.77 |
|
|
|
Ethane***
|
0.89
|
|
|
*Purge gas; **With oxygen; ***With ethylene
References
- The Essential Chemical Industry - Online, 6th Oct 2016, Epoxyethane (Ethylene oxide).
- Wikipedia, Ethylene glycol.
- Intractec Solutions, 31st Aug 2023, Ethylene Glycol Production from Ethylene Oxide (Direct Hydrolysis) | Economic Analysis, medium
- Emad Ali et al., 2022, Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Network of Industrial Ethylene Glycol Plant using Heat Integration based on Pinch Analysis, Polish Journal of Chemical Technology, 24, 2, 8—20, 10.2478/pjct-2022-0009.












.png)
.png)






