Process Summary
The organic peroxide method, also known as the hydroperoxide method, is a widely used industrial process for producing propylene oxide (PO). This method was first developed in the 1970s by Halcon Corp. and Atlantic Richfield Oil Corp. (ARCO). It involves the indirect epoxidation of propylene using organic peroxides such as ethylbenzene hydroperoxide (EBHP) or tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP). The process co-produces valuable by-products: styrene monomer (SM) in the SMPO process or tert-butanol (TBA) in the TBA process. A newer route involves cumene hydroperoxide (CMHP) that produces propylene oxide without generating co-products but instead cumene is recovered and reuse in the process.
SMPO Process (PO/SM Method)
The SMPO process uses ethylbenzene as a feedstock to produce PO and SM.

The key steps are as follows:
1. Ethylbenzene Epoxidation
- Ethylbenzene is oxidized with air to produce ethylbenzene hydroperoxide (EBHP).
- Catalysts: Molybdenum-based homogeneous catalysts or titanium-silica-supported heterogeneous catalysts are used to enhance selectivity.
2. Epoxidation
- EBHP reacts with propylene in an epoxidation reactor, producing PO and o-methylbenzyl alcohol as intermediates.
3. Dehydration
Co-Product Ratio
TBA Process (PO/TBA Method)
The TBA process uses isobutane as a feedstock to produce PO and TBA.

The key steps are as follows:
1. Isobutane Epoxidation
- Isobutane is oxidized with air to form tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP).
2. Oxidation
- TBHP reacts with propylene in an epoxidation reactor, producing PO and TBA as co-products.
3. TBA Utilization
Co-Product Ratio
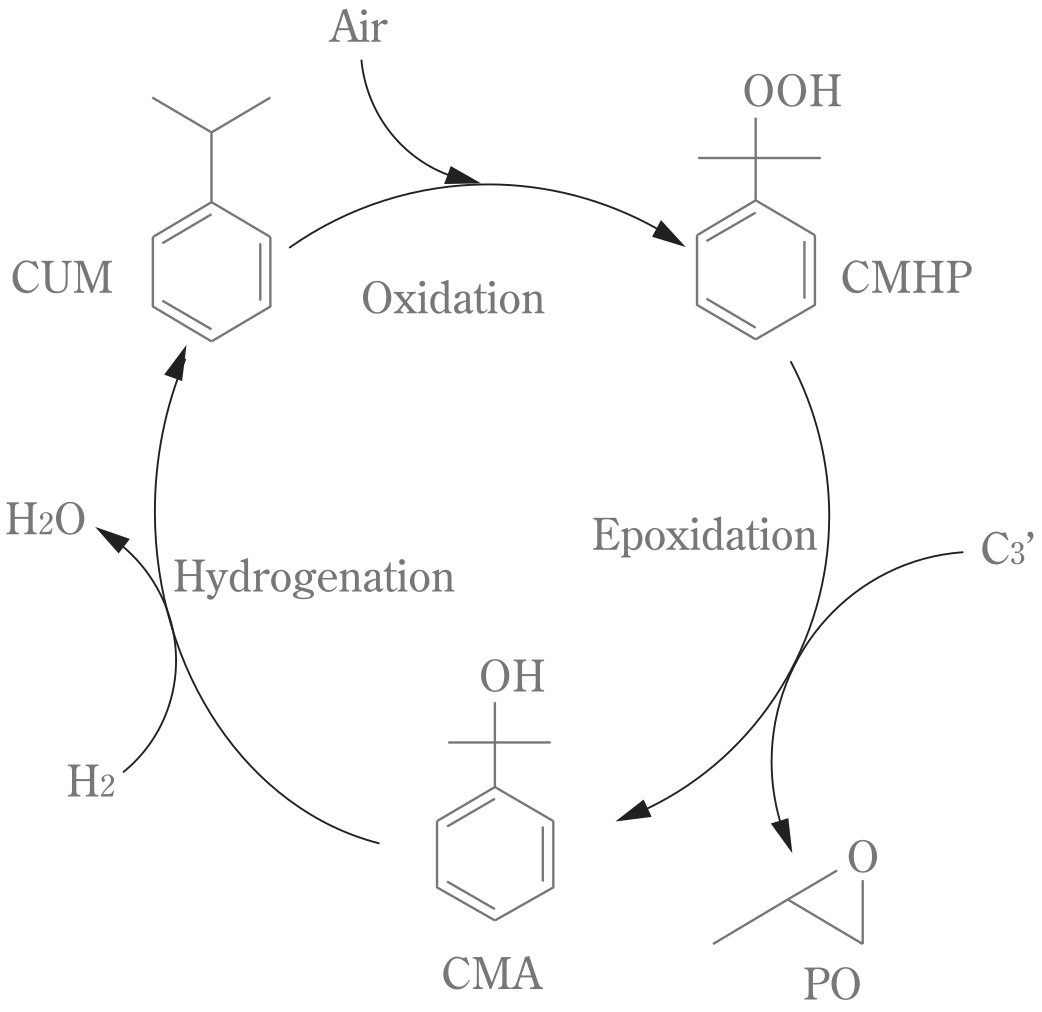
Cumene PO Process
The Cumene PO Process uses Cumene (Isopropylbenzene).
The process involves the following steps:
1. Cumene oxidation
- Cumene is oxidized with air to form cumene hydroperoxide (CMHP)
2. Epoxidation
- CMHP reacts with propylene to form propylene oxide and α,α-dimethylbenzyl alcohol (CMA).
3. CMA conversion
- The CMA by-product is hydrogenated back to cumene, which is recycled to the oxidation step.
Comparison of SMPO, TBA and Cumene Methods
| Feature |
SMPO/PO-SM
Method |
TBA
Method |
Cumene Method |
| Feedstock |
Ethylbenzene |
Isobutane |
Cumene |
| Organic Peroxide |
Ethylbenzene Hydroperoxide (EBHP) |
Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide (TBHP) |
Cumene Hydroperoxide (CMHP) |
| Co-Product |
Styrene Monomer (SM) |
Tert-Butanol (TBA) |
none |
| Co-Product Ratio |
2.5 tons SM per ton PO |
2.1 tons TBA per ton PO |
n.r. |
| Application of Co-Product |
Plastics, rubber manufacturing |
MTBE production, gasoline additive |
n.r. |
| Environmental Impact |
No chlorine,
ome waste |
No chlorine,
some waste |
No chlorine/salt, low CO2 |
| Economic Sensitivity |
Dependent on styrene market demand |
Dependent on
MTBE market demand |
Dependent on PO demand only |
Market Considerations
Both SMO and TBA methods are efficient and environmentally friendly but face challenges due to market dependencies:
- The SMPO method relies on strong demand for styrene monomer, primarily used in plastics like polystyrene and ABS resins.
- The TBA method depends on demand for fuel additives like MTBE, which has declined in some regions due to environmental regulations.
As a result, various producers have developed PO-only processes, such as the Cumene method and direct oxidation (via hydrogen peroxide or direct oxidation), which have been gaining traction due to their single-product focus and reduced reliance on co-product markets.
References
- Tomonori KAWABATA et al., Trends and Views in the Development of Technologies for Propylene Oxide Production, R&D Report SUMITOMO KAGAKU, vol. 2019.
- Junpei T SUJI et al., Development of New Propylene Oxide Process, R&D Report SUMITOMO KAGAKU, vol. 2006-I.
- SULE KALYONCU, Sep 2012, Catalytic Reaction of Propylene to Propylene Oxide on various Catalysts, Middle Est Technical University.














