Technology overview
- HEXSIB is SIBUR's proprietary ethylene trimerization technology for on-purpose production of 1-hexene, developed at NIOST (one of SIBUR's main R&D centers) and licensed globally by Technip Energies.
- The technology employs a chromium-based homogeneous catalyst system with innovative microwave activation to selectively trimerize ethylene to polymer-grade 1-hexene at exceptional selectivity (>99.7%) under mild operating conditions.
Catalyst System Description
Core Catalyst Composition (per US10508065B2 and US11291982B2)
The HEXSIB catalyst system comprises four essential components:
- 1. Chromium source compound
- Trivalent chromium compounds are preferred
- Common chromium sources include chromium(III) chloride, chromium(III) acetate, chromium carboxylates, and organochromium complexes
- Molar ratios are optimized based on the specific chromium compound selected
- 2. Nitrogen-containing ligand (pyrrole compound)
- Pyrrole or substituted pyrrole derivatives serve as the primary ligand
- The pyrrole:Cr molar ratio ranges from 3:1 to 7:1, optimally around 4:1 to 6:1
- The nitrogen-containing ligand coordinates with chromium to form the active catalytic species
- 3. Alkylaluminum compound (activator/cocatalyst)
- Trialkylaluminum compounds such as triethylaluminum (TEA), triisobutylaluminum (TIBA), or tri-n-octylaluminum
- Al:Cr molar ratio ranges from 5:1 to 200:1, typically 10:1 to 100:1
- The alkylaluminum serves dual roles: activator and scavenger for trace impurities
- 4. Zinc compound (performance enhancer)
- Zinc halides (ZnCl₂, ZnBr₂) or organozinc compounds
- Zn:Cr molar ratio typically 1:1 to 10:1
- Zinc incorporation significantly improves catalyst activity, selectivity, and stability
Innovative Microwave Activation (SIBUR Patent Innovation)
A key differentiating feature of HEXSIB is microwave irradiation of catalyst components, particularly the alkylaluminum compound:
- Microwave treatment parameters:
- The alkylaluminum compound is irradiated with microwave (ultra-high frequency, UHF) radiation prior to mixing with other catalyst components
- Microwave frequency: typically 2.45 GHz (standard industrial microwave frequency)
- Irradiation duration: seconds to minutes, typically optimized for each specific formulation
- Temperature control during irradiation prevents decomposition
- Mixing with chromium compound occurs within 10 minutes of microwave treatment to preserve activated state
- Benefits of microwave activation:
- Significantly enhanced catalyst activity (2-5× improvement reported)
- Improved selectivity to 1-hexene
- Better catalyst stability and longer active lifetime
- Enables operation at lower ethylene pressures (as low as 20-40 bar vs. 50+ bar for conventional systems)
Catalyst Preparation Sequence
- Microwave irradiate alkylaluminum compound under controlled conditions
- Within 10 minutes, mix irradiated alkylaluminum with chromium source
- Add pyrrole compound to form chromium-pyrrole complex
- Introduce zinc compound to complete catalyst system
- Dilute with reaction solvent if necessary
- Feed continuously or batch-wise to reactor
Reaction Chemistry and Mechanism
Trimerization Reaction
The selective ethylene trimerization follows a metallacycle mechanism characteristic of chromium-pyrrole catalyst systems:
Overall reaction:
3 C2H4 → C6H12 (1-hexene)
Reaction characteristics
- Highly selective for 1-hexene formation via chromacyclic intermediates
- Exothermic reaction: ΔH ≈ -180 to -200 kJ/mol
- Minimal formation of C₄ (1-butene) or C₈+ oligomers
- Polymer formation suppressed by optimized catalyst design and operating conditions
Selectivity Performance
SIBUR patents claim exceptional selectivity:
- 1-Hexene isomeric purity: ≥99.7% (ratio of 1-hexene to other hexene isomers ≥99.7:0.3)
- 1-Hexene selectivity in C6 fraction: >99.9% achieved with optimized catalyst system
- Overall selectivity to C6 (hexenes): 85-95% based on ethylene converted
- C₄ (butenes) formation: <3%
- C₈+ (higher oligomers): <5%
- Polyethylene formation: Minimized through process control
This exceptional selectivity is a key HEXSIB differentiator and simplifies downstream separation.
Feed Specifications
Ethylene purity requirements
- Polymer-grade ethylene (>99.9% purity)
- Oxygen content: <5 ppm (preferably <1 ppm)
- Water content: <5 ppm
- Sulfur compounds: <1 ppm
- Acetylene and other poisons: minimized through feed purification
Process Configuration and Operating Conditions
Reactor System
Reactor type:
- Liquid-phase stirred tank reactor (CSTR) or loop reactor configuration
- Continuous operation for commercial scale
- Temperature control via external cooling or internal heat exchange
Solvent/diluent:
- Hydrocarbon solvents: toluene, xylenes, cyclohexane, or aliphatic hydrocarbons (C₆-C₁₂)
- 1-Hexene can serve as reaction medium (autogenous solvent)
- Solvent selection impacts selectivity and heat management
Operating parameters
Operating conditions (per SIBUR patents):
| Parameter |
Range |
Typical/Optimal |
| Temperature |
0-120°C |
40-90°C |
| Pressure |
20-150 bar |
30-70 bar |
| Ethylene partial pressure |
15-100 bar |
25-50 bar |
| Residence time |
10-120 minutes |
30-60 minutes |
| Catalyst concentration |
0.01-1.0 mmol Cr/L |
0.05-0.5 mmol Cr/L |
Key advantages of HEXSIB operating window:
- Lower temperature and pressure versus competing technologies
- Milder conditions reduce capital equipment requirements
- Lower energy consumption
- Improved safety profile
Reaction Performance Metrics
Catalyst productivity:
- 50,000-500,000 g 1-hexene per g Cr (highly dependent on conditions)
- Turnover frequency (TOF): 10,000-100,000 mol ethylene converted per mol Cr per hour
- Enhanced by microwave activation
Ethylene conversion per pass:
- Single-pass conversion: 30-70%
- Unreacted ethylene recycled to reactor
- Overall ethylene utilization: >99%
Equipment List
A detailed equipment list is proposed in the Appendix.
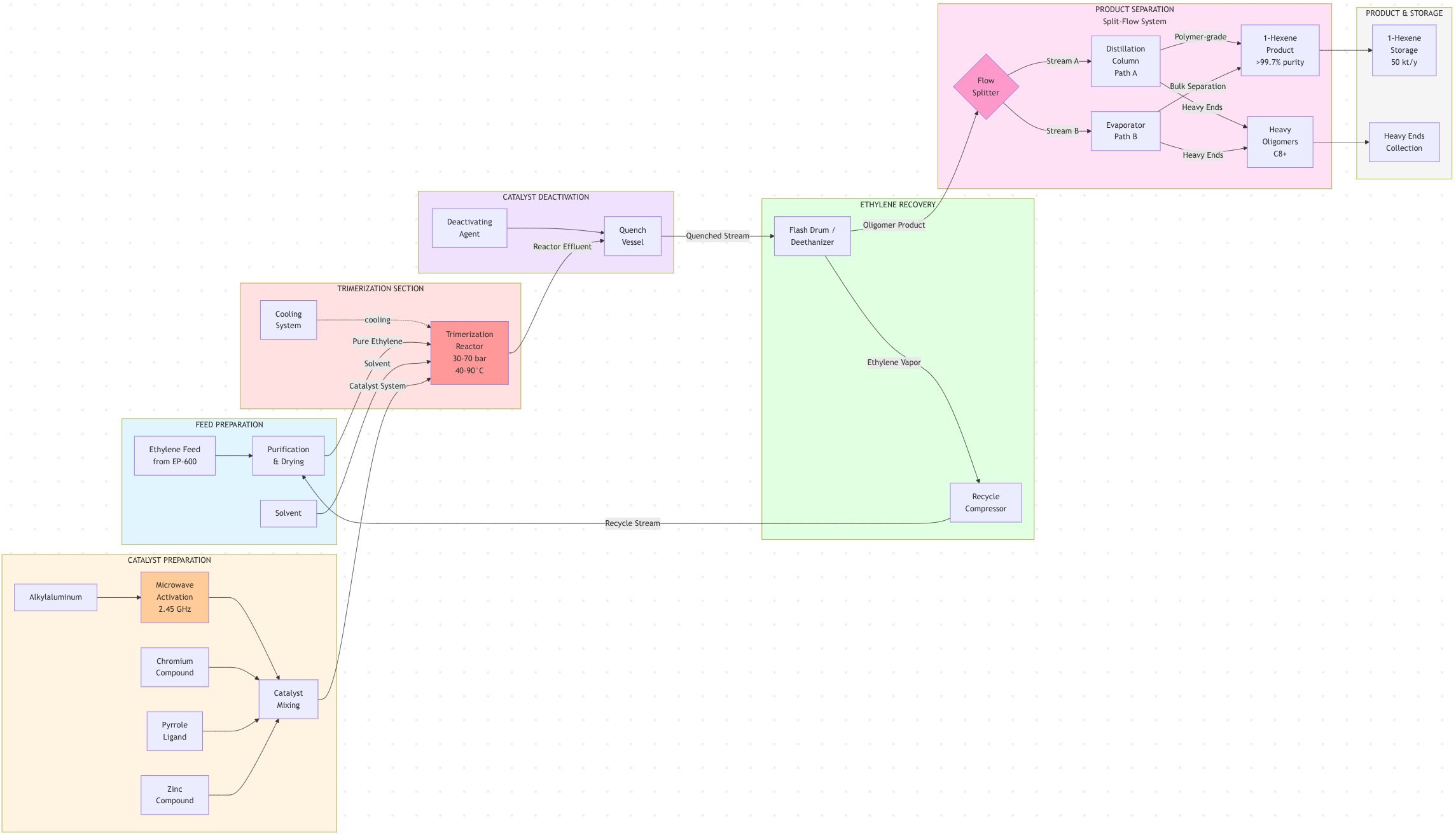
Separation and Product Work-Up (per US11912658B2)
SIBUR's separation patent (US11912658B2) describes an innovative split-flow separation scheme optimized for the HEXSIB process:
- Catalyst deactivation and quench
- Reaction mass discharged from oligomerization reactor
- Contacted with catalyst deactivating agent (alcohol, water, or alkaline solution)
- Rapid quench stops reaction and stabilizes product slate
- Primary ethylene recovery
- Flash separation or distillation removes unreacted ethylene
- Ethylene recycle stream returned to reactor feed after compression/purification
- Oligomerization product stream proceeds to further fractionation
- Split-flow separation (SIBUR innovation)
The patent describes a key innovation: splitting the oligomerization product stream into two parallel processing paths:
→ Path A: Part of product to distillation column for high-purity fractionation
→ Path B: Part of product to evaporator for bulk separation with lower fouling risk
This split-flow design minimizes polymer contamination of equipment and extends run lengths between cleaning cycles.
- 1-Hexene product isolation
- Distillation column(s) separate 1-hexene from:
- Lighter components (C₄, C₅ if present)
- Heavier components (C₈+, solvent)
- Multiple distillation stages achieve polymer-grade 1-hexene specification
- Evaporator handles streams with higher polymer/heavy oligomer content
- Heavy ends management
- C₈+ oligomers and trace polymer removed as bottoms
- Minimal heavy ends due to high front-end selectivity
- Solvent recovery and recycle where applicable
Product Specifications
Polymer-grade 1-hexene (HEXSIB product):
| Property |
Specification |
| 1-Hexene purity |
>99.7% (>99.9% achievable) |
| Other C₆ isomers |
<0.3% |
| C₄ and lighter |
<100 ppm |
| C₈ and heavier |
<500 ppm |
| Water |
<50 ppm |
| Peroxides |
<10 ppm |
| Color |
Water-white |
This product meets requirements for all commercial PE catalyst systems (Ziegler-Natta, metallocene, chromium, single-site).
Plant Configuration: Nizhnekamskneftekhim (NKNH) Implementation
Project Overview
SIBUR's first commercial HEXSIB unit is at Nizhnekamskneftekhim (NKNH) in Tatarstan, Russia:
- Capacity: 50,000 tonnes/year 1-hexene
- Feed integration: Ethylene from EP-600 olefins complex (1,500 kt/y ethylene cracker)
- Timeline: Construction completed end-2024, commissioning 2024-2025, commercial operation 2025
- Strategic purpose: Replace imported 1-hexene (previously sourced from UK and Germany); supply 125-130% of SIBUR's internal demand

Process Integration
- Direct ethylene pipeline from EP-600 to HEXSIB unit
- Closed-loop water circulation system for cooling
- Closed flare system for emissions control (low-carbon design)
- 1-Hexene product storage and distribution to SIBUR PE plant
Technology Performance Summary
Key Performance Indicators
| Metric |
HEXSIB Performance |
Industry Benchmark |
| 1-Hexene selectivity |
>99.7% isomeric purity |
95-99% |
| C₆ selectivity (on ethylene) |
85-95% |
80-90% |
| Operating pressure |
30-70 bar |
50-100+ bar |
| Operating temperature |
40-90°C |
80-120°C |
| Catalyst productivity |
50,000-500,000 g/g Cr |
Variable |
| Energy efficiency |
High (mild conditions) |
Moderate to high |
| Capital intensity |
Lower (simpler equipment) |
Higher |
Technology Advantages (per SIBUR/Technip statements)
- Milder operating conditions: Lower T/P reduce equipment cost and energy use
- Exceptional selectivity: >99.7% 1-hexene purity simplifies separation
- High catalyst performance: Microwave activation enhances activity and stability
- Simplified separation: High selectivity reduces fractionation complexity
- Lower carbon footprint: Energy efficiency and potential for bio-based ethylene feedstock
- Drop-in compatibility: Product meets all PE catalyst system requirements
- Proven scale-up: Commercial unit operating at NKNH
Techno-Economic Positioning
Competitive Advantages
- vs. Full-range α-olefin processes: HEXSIB is dedicated to 1-hexene, avoiding co-product balance issues
- vs. Other trimerization routes: Microwave activation and zinc enhancement improve economics
- vs. Imported 1-hexene: Integrated production reduces logistics costs and supply risk
Market and Licensing Strategy
- Internal use: SIBUR PE plants (LLDPE/HDPE specialty grades)
- External licensing: Technip Energies offers HEXSIB to global polyolefin producers
- Integration opportunities: Can be incorporated into greenfield PE complexes or retrofitted to existing sites
References
SIBUR Patents (Ethylene Trimerization to 1-Hexene)
- US10508065B2 (granted Dec 17, 2019): Methods of preparing oligomers of an olefin. Inventors: Zilbershtein TM, Lenev DA, Lipskikh MV. Assignee: SIBUR Holding PJSC.
- US11291982B2 (granted Apr 5, 2022): Catalyst system used in olefin oligomerization and method for olefin oligomerization. Inventors: Lenev DA, ACEVEDO FORERO R. Assignee: SIBUR Holding PJSC.
- US11912658B2 (granted Feb 27, 2024): Method for separating olefin oligomerization products (variants). Inventors: Arkatov OL, Lipskikh MV, Popov EA, Khusainov AF. Assignee: SIBUR Holding PJSC.
- US8921251B2 (granted Dec 30, 2014): Catalyst system and processes for the (co-)trimerization of olefins and the (co-)polymerization of olefin oligomers. Inventors: Zilbershtein TM, Lipskikh MV, Nosikov AA, Nesyn GV. Assignee: SIBUR Holding PJSC.
SIBUR and Technip Energies Communications
- SIBUR. SIBUR's speciality chemical tech used in premium basic polymer production goes international. Press release | Jan 12, 2022
- Technip Energies and SIBUR. Technip Energies and SIBUR announce agreement to license lower-carbon HEXSIB technology. Joint press release | Jan 11, 2022
- Interfax. SIBUR to produce up to 50,000 tpy of hexene at Nizhnemkamskneftekhim. Aug 31, 2022.
- PGCA/NANGS. Sibur will start switching to its own hexene in 2025 from the installation at NKNH. Apr 22, 2024.
- Interfax. SIBUR receives first hexene product from NKNK facility. Aug 25, 2025.
Feed Preparation and Storage Section
Ethylene Feed System
- Ethylene feed compressor(s) (integration from EP-600 or external supply)
- Ethylene storage sphere or pressure vessel
- Ethylene vaporizer (if LPG feed)
- Ethylene dryer (molecular sieve beds)
- Ethylene purification guard beds (oxygen, sulfur, acetylene removal)
- Ethylene feed pump(s)
- Feed gas preheater
Solvent/Diluent System
- Solvent storage tank(s)
- Solvent distillation/purification column
- Solvent circulation pumps
- Solvent makeup system
Catalyst Preparation Section
Microwave Activation Unit (SIBUR Innovation)
- Microwave irradiation reactor/chamber (2.45 GHz, UHF)
- Alkylaluminum feed vessel (inert atmosphere)
- Temperature control system for microwave chamber
- Inert gas (nitrogen/argon) supply system
Catalyst Mixing and Feed System
- Chromium compound storage vessel (inert atmosphere)
- Pyrrole compound storage vessel (inert atmosphere)
- Zinc compound storage vessel (inert atmosphere)
- Alkylaluminum storage vessel (inert atmosphere)
- Catalyst component mixing vessel(s) with agitation
- Catalyst dilution vessel
- Precision metering pumps for each catalyst component (4-6 streams)
- Catalyst feed accumulator
- Inert gas blanketing system
Reaction Section
Primary Reactor System
- Ethylene trimerization reactor (liquid-phase CSTR or loop reactor)
- Internal or external cooling system
- High-efficiency agitator (for CSTR)
- Temperature control jacket or internal coils
- Pressure control system
- Multiple feed injection points (ethylene, catalyst, solvent)
- Reactor circulation pump (for loop configuration)
- Emergency pressure relief system
- Reactor effluent heat exchanger(s)
Heat Management
- Reaction heat removal system (cooling water or refrigerant)
- Process cooling water circulation pumps
- Closed-loop cooling water system (NKNH implementation)
Catalyst Deactivation and Quench Section
Quench System
- Catalyst deactivation/quench vessel
- Deactivating agent storage tank (alcohol, water, or alkaline solution)
- Deactivating agent injection pump
- Flash drum for initial vapor-liquid separation
- Quench effluent cooler
Ethylene Recovery and Recycle Section
Ethylene Separation
- Primary flash drum or deethanizer column
- Ethylene recycle compressor
- Recycle ethylene cooler
- Recycle ethylene dryer (if needed)
- Ethylene recycle surge drum
Product Separation and Purification Section
Split-Flow Separation System (SIBUR Patent US11912658B2)
Path A - Distillation Train
- Light ends removal column (C₄/C₅ separation if present)
- 1-Hexene purification column (main fractionator)
- Reboiler
- Condenser
- Reflux drum
- Reflux pump
- Column internals (trays or structured packing)
- Heavy ends stripper (C₈+ removal)
- Product cooler(s)
- Distillate receiver
Path B - Evaporator System
- Oligomerization product evaporator
- Evaporator feed pump
- Evaporator heating system
- Vapor-liquid separation vessel
- Evaporator bottoms handling system
Common Equipment
- Product splitter/distribution system (splits flow between paths A & B)
- Intermediate product storage vessels
- Product transfer pumps
Product Finishing and Storage
1-Hexene Product System
- Polymer-grade 1-hexene storage tank(s) (nitrogen blanketed)
- Product stabilization system (antioxidant addition if required)
- Product quality sampling and analysis system
- Product loading pumps
- Loading rack and tanker truck/railcar connections
Heavy Ends and Waste Management
Heavy Oligomer System
- C₈+ heavy oligomer collection vessel
- Heavy ends pump
- Heavy oligomer storage tank
- Disposal or valorization system
Polymer/Solids Handling
- Polymer trap/filter system
- Periodic cleanout equipment
- Waste polymer handling system
Utilities and Support Systems
Heating and Cooling
- Process cooling water system (closed-loop per NKNH design)
- Cooling water circulation pumps
- Cooling towers or heat exchangers
- Steam system (for reboilers and heating)
- Refrigeration system (if sub-ambient cooling required)
Compressed Gas Systems
- Nitrogen generation or supply system
- Instrument air compressor and dryer
- Plant air compressor
Flare and Safety Systems
- Closed flare system (NKNH low-emission design)
- Flare knockout drum
- Emergency relief headers
- Safety relief valves (on all pressure vessels)
- Flame arrestors
Electrical and Instrumentation
- Distributed Control System (DCS) or PLC
- Process analyzers:
- Online gas chromatograph(s) for product composition
- Ethylene purity analyzer
- Oxygen analyzer
- Moisture analyzer
- Temperature transmitters and controllers
- Pressure transmitters and controllers
- Flow meters (Coriolis, magnetic, orifice plate)
- Level transmitters
- Control valves (temperature, pressure, flow control)
- Motor control centers (MCC)
- Electrical substations and distribution
Fire Protection and Safety
- Fire water system and pumps
- Fire detection and alarm system
- Gas detection system (hydrocarbon, toxic gas)
- Emergency shutdown system (ESD)
- Safety instrumented systems (SIS)
- Personal protective equipment stations
Equipment Count Summary (Typical 50 kt/y Unit)
Equipment Category | Approximate Count
| Equipment Category |
Approximate Count |
| Vessels and reactors |
15-25 |
| Distillation columns |
2-4 |
| Heat exchangers |
15-30 |
| Pumps |
20-40 |
| Compressors |
2-4 |
| Storage tanks |
8-15 |
| Process analyzers |
5-10 |
| Control valves |
50-100 |
This equipment list represents a typical HEXSIB plant configuration based on the 50,000 t/y NKNH implementation and SIBUR patent disclosures.