Visbreaking (viscosity reduction, viscosity breaking) is a mild form of residual oil thermal cracking.
The purpose of the visbreaker in an oil refinery is to reduce the quantity of residual oil produced in the distillation of crude oil and to increase the yield of more valuable middle distillates (heating oil and diesel) by the refinery. A visbreaker thermally cracks large hydrocarbon molecules in the oil by heating in a furnace to reduce its viscosity and to produce small quantities of light hydrocarbons (LPG and gasoline).
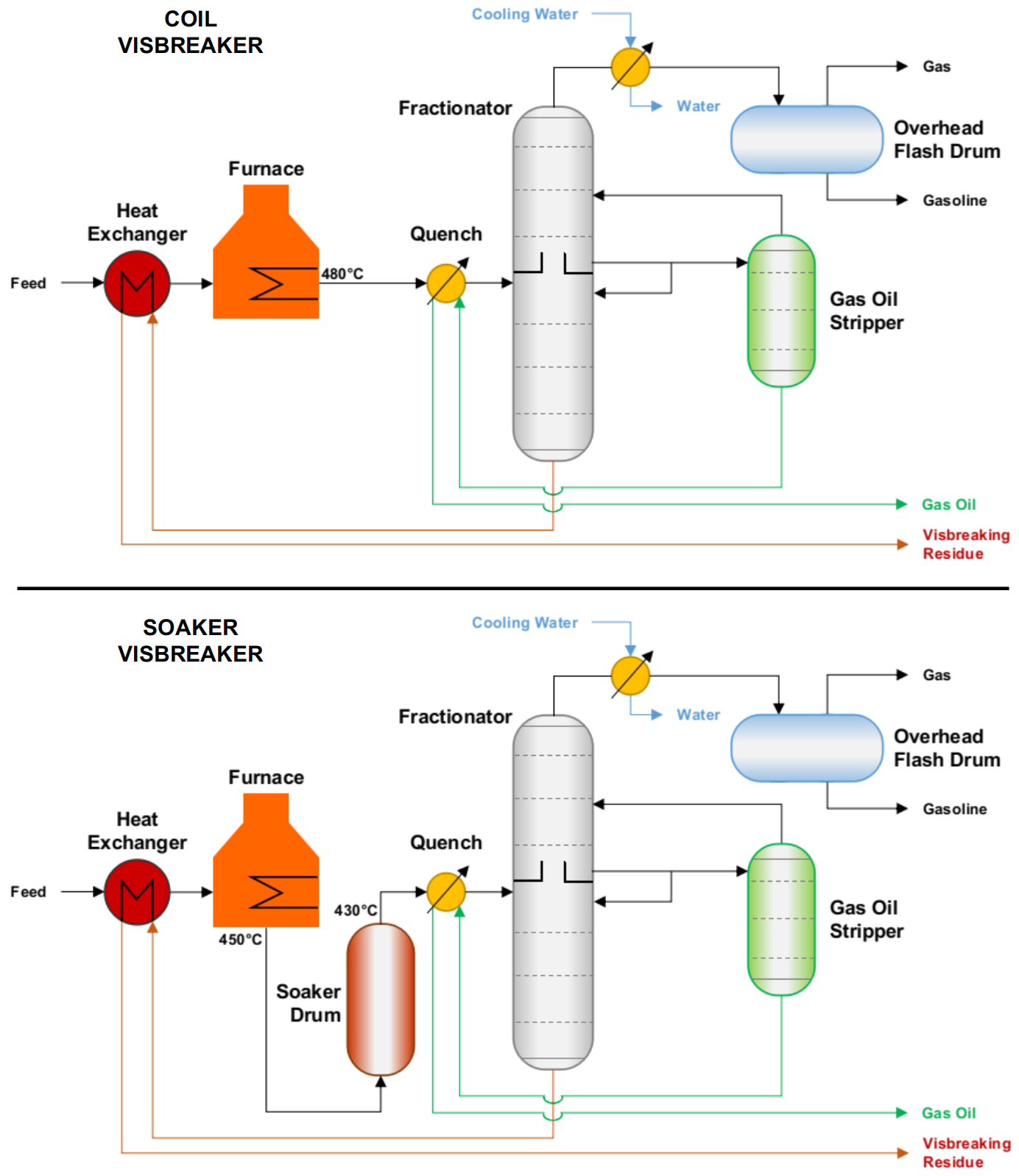
Two visbreaking processes are commercially available: the Soaker Visbreaker and the Coil Visbreaker:
- Coil Visbreaking Process (high temperature, short residence time process)
The term coil (or furnace) visbreaking is applied to units where the cracking process occurs in the furnace tubes (or "coils"). Material exiting the furnace is quenched to halt the cracking reactions: frequently this is achieved by heat exchange with the virgin material being fed to the furnace. The extent of the cracking reaction is controlled by regulation of the speed of flow of the oil through the furnace tubes.
- Soaker Visbreaking Process (low temperature, high residence time process)
In soaker visbreaking, the bulk of the cracking reaction occurs not in the furnace but in a drum located after the furnace called the soaker. Here the oil is held at an elevated temperature for a pre-determined period of time to allow cracking to occur before being quenched. In soaker visbreaking, lower temperatures are used than in coil visbreaking. A comparatively long duration of the cracking reaction is applied instead.
The oil produced by the visbreaker is passed to a fractionnator where the products of the cracking (gas, LPG, gasoline, gas oil and tar) are separated and recovered.[1]
The yields of the various hydrocarbon products will depend on the "severity" of the cracking operation as determined by the temperature the oil is heated to in the visbreaker furnace. At the low end of the scale, a furnace heating to 425 °C would crack only mildly, while operations at 500 °C would be considered as very severe. Arabian Light Crude residue when visbroken at 450 °C would yield around 76% (by weight) of Tar, 15% middle distillates, 6% gasolines and 3% gas and LPG.[2]
1. Visbreaker, Wikkipedia
2. Visbreaking, Citizendium